Breastfeeding infants repeatedly for six months in the course of the wet season, with out together with some other meals, might assist forestall a illness linked to micronutrient deficiencies, a examine suggests.
The illness, known as environmental enteric dysfunction (EED), is widespread amongst youngsters in low-income settings and is linked to poor sanitation, micronutrient deficiencies and low top in youngsters, the examine says.
“Unique breastfeeding protects towards environmental enteric dysfunction, particularly whether it is launched in the course of the wet season,” says James Berkley, a co-author of the examine and professor of pediatric infectious illness on the College of Oxford in England. “Meals aside from breast milk usually tend to be contaminated in the course of the wet season.”
Berkley says the analysis signifies that poor progress and frequent sickness stay widespread in resource-poor nations and might be linked to environmental enteric dysfunction.
“We have no idea the reason for environmental enteric dysfunction or when it first begins in childhood,” he tells SciDev.Internet. “We needed to see if irregular progress of micro organism within the higher small bowel and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth could be accountable, together with wanting [for] different potential exposures like infections, antibiotics, and breastfeeding,” Berkley says. “The findings present that stopping unique breastfeeding was strongly related to [the] illness.”
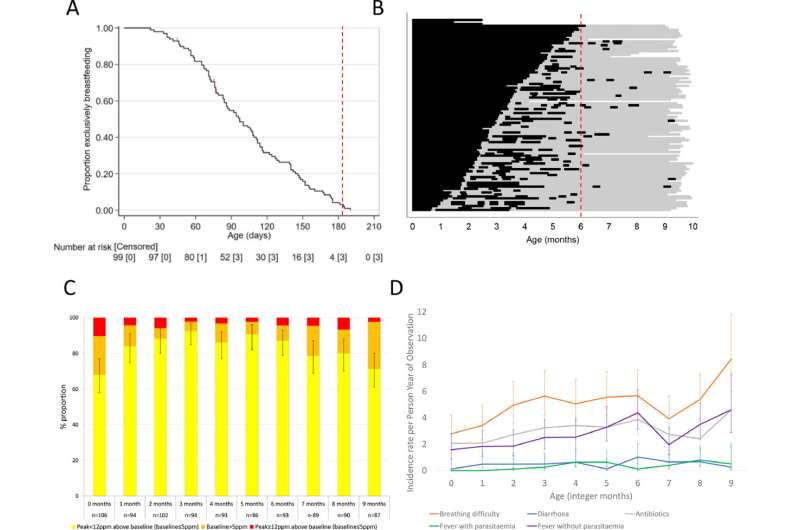
The researchers studied 100 infants at start in Junju—a settlement in rural coastal Kenya—from August 2015 to January 2017, and examined every toddler for 9 months. The infants had been periodically assessed for progress and totally different indices akin to weight-reduction plan, breastfeeding, sickness episodes and medicine.
“Through the wet season, diarrhea, fever and respiration problem occurred extra regularly, [and] markers of EED had been worse,” says the examine printed in eClinicalMedicine final month (21 April). “We heard from contributors’ caregivers that complementary meals consumed in the course of the wet season have often been saved for longer and should subsequently be at greater danger of bacterial or fungal toxin contamination or lack of nutrient worth.”
Goodness Anyanwu, a nutritionist on the Federal Ministry of Well being, Nigeria, tells SciDev.Internet that the six-month interval of unique breastfeeding enhances toddler intestine maturity earlier than the introduction of complementary feeding.
“The angle of intensifying unique breastfeeding in the course of the wet season, particularly for infants born in that interval to forestall enteric contamination from grains saved over a very long time is revealing,” says Anyanwu. “It reveals that for kids above six months, predominant breastfeeding needs to be a precedence in the course of the wet season.”
She recommends that the examine is used as an advocacy device for the World Breastfeeding Week that occurs globally each August. “Outcomes of analysis akin to this needs to be integrated into vitamin training modules, each within the rural communities and concrete areas. It should even be useful on the nationwide and Sub-Saharan [Africa] degree,” she says.
Berkley provides that households and nutritionists needs to be made conscious of the chance of early discontinuation of breastfeeding, which is best in the course of the wet season.
Rosie J. Crane et al, Cessation of unique breastfeeding and seasonality, however not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, are related to environmental enteric dysfunction: A start cohort examine amongst infants in rural Kenya, eClinicalMedicine (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101403
Supplied by
SciDev.Internet
Quotation:
Breastfeeding in wet season ‘wards off illness’ (2022, Might 17)
retrieved 17 Might 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-05-breastfeeding-rainy-season-wards-disease.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.









