
The typical physique incorporates about 37 trillion cells—and we’re within the midst of a revolutionary quest to know what all of them do. Unraveling this requires the experience of scientists from all completely different backgrounds—laptop scientists, biologists, clinicians and mathematicians—in addition to new expertise and a few fairly subtle algorithms.
The place as soon as a primitive microscope, basically little greater than a magnifying glass, would reveal a brand new cell instantly and viscerally—in the identical method that Antonie van Leeuwenhoek found sperm in 1677—at this time it’s evaluation on a pc display screen which brings us such revelations. However it’s simply as fantastic.
Any such analysis is difficult in all types of the way—from the science itself to the sociology of enormous groups engaged on it—however the pay-off could be large. It definitely was for a consortium of 29 scientists who got down to decide which sorts of cells make up the liner of the trachea, or windpipe—and stumbled upon a brand new kind of cell that would remodel our understanding and remedy of cystic fibrosis.
The primary time the staff—co-led by Aviv Regev on the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard—got here throughout these cells, they had been taking a look at an evaluation of 300 cells within the trachea of mice. Three cells did not appear to correspond to something that had been seen earlier than. Had it been simply two, they could have dismissed it as an consequence of noise within the knowledge—however three unusual cells warranted a better look.
In lab banter, they grew to become often called the “scorching cells.” The scientists repeated the experiment a number of instances, and it quickly grew to become clear they actually had stumbled upon a brand new kind of cell within the trachea.
Because it turned out, one other staff from the US and Switzerland had independently discovered the identical factor. The 2 groups learnt of one another’s work by likelihood at a seminar in 2017. “It was a type of stunning moments in science,” recalled Moshe Biton from the Broad Institute staff, “when two teams discovered the identical outcomes individually.”
Each teams confirmed that these new cells exist within the human airways in addition to in mice and, after assembly up, agreed to publish their two papers side-by-side. These new cells had not been seen earlier than, just because they’re so uncommon—they make up round 1% of cells within the airway. However that does not imply they’re unimportant. When the 2 groups regarded intimately at what made these cells stand out, they got here throughout one thing astonishing.
One of many genes lively in these new-found trachea cells turned out to be CFTR—the “cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator” gene. This gave their work an entire different degree of that means as a result of mutations on this gene trigger cystic fibrosis.
Precisely how this illness is brought on by the inheritance of a dysfunctional model of the CFTR gene has been a thriller ever because the hyperlink was found in 1989. Cystic fibrosis is a fancy illness, normally starting in childhood, with signs typically together with lung infections and problem respiratory. There are therapies however no remedy.
Now it appears potential that the important thing to understanding the trigger might lie in understanding what these newly found cells do, and what occurs to those cells if the CFTR gene is flawed. The analysis continues.
However already from this discovery, and different analysis utilizing comparable strategies, there’s the sense that our understanding of the physique’s cells is being remodeled by a piercing new mixture of biology and laptop science. And that is the place much more game-changing discoveries are about to be made.
The variety of human cells
Each one of many 37 trillion-or-so cells in your physique is exclusive to some extent. Forms of cell are decided by the actual proteins they include—so solely a pink blood cell has hemoglobin, for instance, and a neuron incorporates completely different proteins from an immune cell. No two cells within the physique include precisely the identical quantities of every protein.
The immune system is particularly advanced. It includes many sorts of cells categorized by their core operate—T cells, B cells and so forth. However there are additionally numerous delicate variations of those T cells and B cells. We do not even actually know what number of variants there are—but when we might perceive what all of them do, we’d higher perceive the immune system. This in flip would allow us to design new medicines to assist the immune system to, for instance, higher battle most cancers.
One form of immune cell that my analysis staff at Manchester College research is known as the pure killer cell. There are a few thousand of those immune cells in every drop of your blood, and they’re particularly good at detecting and killing different cells which have turned cancerous or have turn into contaminated with a virus. Once more, not all pure killer cells are alike. One evaluation has estimated that there are a lot of hundreds of variants of this immune cell in anyone particular person.
In 2020, my analysis lab carried out an evaluation which urged that variants of pure killer cells in blood may very well be organized into eight classes. Whereas their completely different roles within the physique aren’t but absolutely understood, it is possible that some are particularly adept at attacking explicit sorts of virus, others are higher at detecting most cancers, and so forth.
Different sorts of immune cell could be much more various. Evidently, our element cells are as various because the human beings they make up, and understanding how such advanced populations of cells work collectively (on this case, to defend in opposition to illness) is a crucial frontier.
Utilizing the language of algorithms
To penetrate this complexity, the variety of human cells have to be translated into the language of algorithms.
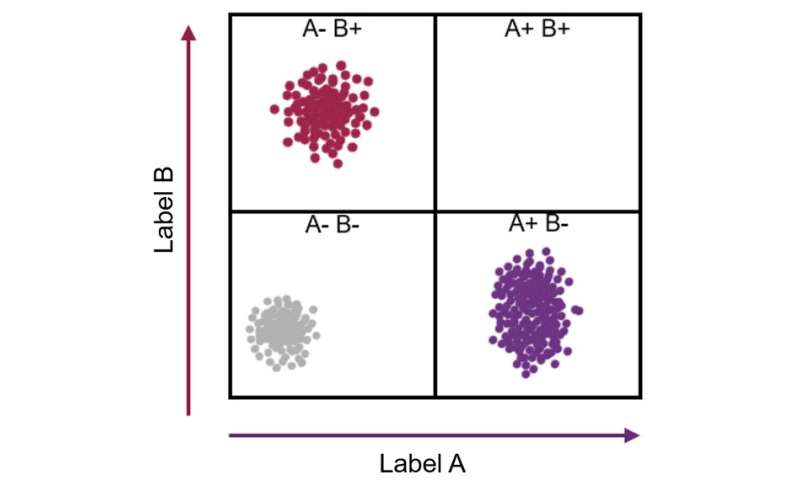
Think about a cell incorporates simply two sorts of protein, X and Y. Each particular person cell could have a certain amount of every of those two proteins. This may be represented as some extent on a graph the place the extent of protein X turns into a place alongside the x-axis, and the extent of protein Y its location alongside the y-axis.
One cell could include a excessive quantity of protein X and slightly of protein Y (which could be revealed by a circulate cytometer displaying that the cell stains with a excessive quantity of 1 antibody and a low quantity of one other antibody). This cell can then be represented as some extent positioned far alongside the x-axis and slightly method up the y-axis.
As every cell takes up a place on the graph, these with comparable ranges of the X and likewise the Y protein—prone to be the identical kind of cell—seem as a cluster of factors. If hundreds or hundreds of thousands of cells are plotted on this method, the variety of discrete clusters that emerge tells us what number of sorts of cells there are. Additionally, the variety of factors inside a cluster tells us what number of cells there are of that kind.
The fantastic factor is that this type of evaluation can reveal what number of sorts of cells are current in, say, a pattern of blood or a tumor biopsy, with out being guided in any method about which cells we expect to seek out. Because of this sudden outcomes can flip up. A cluster of knowledge factors would possibly seem with sudden properties—implicating the invention a brand new form of cell.
In fact, cells want greater than two coordinates to explain them. The truth is, over the past decade, a sort of study—often called single-cell sequencing– has been developed to measure the extent to which particular person cells use every of the 20,000 human genes it incorporates.
Which of them out of all of the 20,000 human genes a specific cell is utilizing—known as the cell’s transcriptome—can then be analyzed to create a “map” of various cells. We won’t think about cells represented on a graph with 20,000 axes, however a pc algorithm can deal with this evaluation in simply the identical method it will one with solely two variables. Related cells are positioned shut collectively, whereas cells utilizing very completely different units of genes are far aside.
Algorithms to do that are borrowed from different fields of science, equivalent to these utilized in analyzing social networks. Then we get to spend days, if not years, mining the output, deciphering what the map means: what number of sorts of cells there are, what defines their variations, and what they do within the physique?
Proper now, this endeavor is going on on an unprecedented scale because of the Human Cell Atlas consortium—resulting in every kind of discoveries concerning the human physique.
The Human Cell Atlas
In October 2016, Regev and Sarah Teichmann from the Wellcome Sanger Institute organized an occasion in London for round 100 world-leading scientists to debate learn how to chart each cell within the human physique. The elevator pitch was to assemble one thing like Google Maps for the physique: “We all know the international locations and foremost cities, now we have to map the streets and buildings.”
A 12 months later, that they had drafted a particular plan—to first attempt to profile 100 million cells from completely different methods and organs, utilizing completely different folks across the globe. Hundreds of scientists in over 70 international locations from each inhabited content material have joined the consortium since—it’s an particularly various neighborhood, appropriately for such an enormous international scientific endeavor.
In some ways, this daring new ambition is a direct descendant of the Human Genome Mission. By sequencing all of the human genes contained in every human cell, formally accomplished in April 2003, all types of genetic variations have been linked to elevated susceptibility to a particular sickness.
Nonetheless, genetic illnesses manifest within the particular cells the place that gene is generally used. So, crucially, an evaluation of genes alone is not sufficient—we additionally must know the place within the human physique these disease-causing genes are being switched on.
The Human Cell Atlas is bridging this hole between summary genetic codes and the physicality of the human physique. We have already seen one instance of how essential that is—the invention of the cystic fibrosis gene being utilized by a brand new, uncommon cell. One other instance comes from what occurs throughout being pregnant.
Unlocking the secrets and techniques of being pregnant
For a few years, we’ve got recognized that the immune system is intimately linked with being pregnant. For instance, some combos of immune system genes are barely extra frequent than can be anticipated by likelihood in {couples} who’ve had three or extra miscarriages. Whereas we do not but perceive why that is, working it out could be medically essential in resolving issues in being pregnant.
To sort out the problem, a consortium of scientists (co-led by Teichmann as a part of the Human Cell Atlas undertaking) analyzed round 70,000 cells from the placenta and lining of the womb from ladies who had terminated their being pregnant at between six and 14 weeks.
The placenta is the organ the place vitamins and gases cross backwards and forwards between the mom and growing child. It was as soon as thought the mom’s immune system have to be switched off within the lining of the womb the place the placenta embeds, in order that the placenta and fetus aren’t attacked for being “alien” (like an unmatched transplant) on account of half the fetus’s genes coming from the daddy. However this view turned out to be incorrect—or too easy on the very least.
We now know, from a wide range of experiments together with this evaluation, that within the womb, the exercise of the mom’s immune cells is considerably lessened, presumably to stop an opposed response in opposition to cells from the fetus, however the immune system will not be switched off. As a substitute, the immune cells we met earlier, pure killer cells, well-known for killing contaminated cells or most cancers cells, tackle a totally completely different, extra constructive job within the womb; serving to construct the placenta.
The scientists’ evaluation of 70,000 cells has additionally highlighted that each one types of different immune cells are additionally essential within the building of a placenta. What all of them do, although, is not but clear—that is on the fringe of our data.
Muzlifah “Muzz” Haniffa is among the three ladies who led this evaluation. As a doctor and scientist, she sees the physique from two views on an nearly each day foundation: as a computational evaluation of cells on a display screen, and as sufferers who stroll by means of the door. Each as stones and the arch they make.
Proper now, these two views do not simply mesh. However in time, they may. Sooner or later, Haniffa thinks the instruments docs use every day—equivalent to a stethoscope to take heed to an individual’s lungs, or a easy blood rely—will likely be changed by devices that profile our physique’s cells. Algorithms will analyze the outcomes, make clear the underlying drawback, and predict one of the best remedy. Many different physicians agree together with her—that is the approaching way forward for well being care.
What this might imply for you
Infants are actually routinely born by IVF, organ transplants have turn into frequent, and general most cancers survival charges within the UK have roughly doubled lately—however all these achievements are nothing to what’s coming.
As I’ve written about in The Secret Physique, progress in human biology is accelerating at an unprecedented fee—not solely by means of the Human Cell Atlas however in lots of different areas too. Evaluation of our genes presents a new understanding of how we differ; the actions of mind cells give clues to how our minds work; new buildings discovered inside our cells result in new concepts for drugs; proteins and different molecules discovered to be circulating in our blood change our view of psychological well being.
In fact, all science has an ever-increasing impression on our lives, however nothing impacts us as deeply or instantly as new revelations concerning the human physique. On the horizon now, from all this analysis, are solely new methods of defining, screening and manipulating well being.
We’re already accustomed to the concept that our private genetic info can be utilized to information our well being. However a quieter—nearly secret—revolution can also be below method and it might have a fair larger impression on the way forward for well being care: deep analytics of the human physique’s cells.
Someday, a watch that may measure a couple of easy issues about your physique will likely be seen as a laughably primitive instrument. Sooner or later, possibly inside ten years or so, an entire cloud of data will likely be out there—together with an evaluation of your physique’s cells—and you’ll have to determine how a lot you need to delve into it. This revolution in human biology will equip us individually with new powers—and we are going to every must determine for ourselves if and when to deploy them.
It’s possible you’ll, for instance, someday go to your physician with one thing irregular in your pores and skin—a rash, itch, or one thing else. The physician could then take a small pattern of your pores and skin, or maybe a blood pattern, and from an entire cell-by-cell evaluation of what is there, be capable to exactly diagnose the issue and know one of the best remedy. Certainly, a few of this would possibly even be automated. Additional into the longer term, if the tools wanted to do that will get small and low cost sufficient, maybe the evaluation may very well be finished by your self at house.
Ailments can even be extra ceaselessly predicted earlier than any signs are current in any respect. In fact, this is among the most important missions of science: to cease human illness earlier than it even begins. For some sicknesses, this has been achieved already—with vaccines, clear water and improved sanitation. Now, with the human physique opening as much as us by means of computational evaluation of cells, genes and extra, new methods of pre-empting illness are rising. We’re compelled to grab this new alternative—but in observe, there are challenges and unintended penalties to deal with.
Take a well-recognized instance: the thought of the body-mass index, a worth derived from an individual’s weight and top. That is used to label us as underweight, regular weight, chubby or overweight. It is helpful because it signifies an elevated danger of well being issues arising, equivalent to kind 2 diabetes, and steps could be taken to scale back the probability of this occurring. However the label itself also can set off different types of issues referring to an individual’s self-worth, and the way society views weight problems and human range.
Troublesome choices about how you reside
Each one in every of us is vulnerable to some illness or different, to some extent. In order science progresses and we study increasingly about ourselves, we are going to absolutely all discover ourselves drowning in knowledge about ourselves, awash with estimates and chances that play video games with our thoughts and our identification, and require us to make troublesome choices about our well being and the way we dwell.
It appears possible, for instance, that the state of an individual’s immune system, analyzed in depth, might assist predict the signs they’re prone to have if contaminated with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, for instance. Markers of immune exercise would possibly even correlate with an individual’s psychological well being. One evaluation concluded that exact pro-inflammatory secretions from immune cells (known as cytokines) are discovered at greater ranges in people who find themselves depressed.
As we study concerning the composition and standing of the human physique, this may inevitably set up new methods of assessing well being. And it might very nicely assist resolve issues in being pregnant too, as we have seen. However there are issues right here too—if an evaluation suggests an opportunity of an issue, say 50%, how would you act on this info if the medical intervention that would assist has its personal dangers too?
There’s seemingly no finish to how the metric evaluation of the human physique will result in essential however advanced new well being choices. Angelina Jolie famously acted on genetic info when she had each of her breasts surgically eliminated in 2013, and later her ovaries and fallopian tubes, following a genetic check which established that she had inherited a specific variation in a gene often called BRCA1. Crucially, she had been given a really excessive—87%—likelihood of growing breast most cancers. Normally, dangers and chances about our well being are a lot much less clear than this.
So the query arises, how are we to behave on all this new info? What if one thing has been recognized which means your danger of growing an autoimmune illness or most cancers is one in six within the subsequent ten years? Wouldn’t it be completely different if it was one in 4? At what level would you determine to take drugs as a precaution, or bear surgical procedure, understanding that in addition they carry their very own dangers? And would this data in itself make you are feeling in poor health? Would your identification be affected?
I haven’t got the solutions—however that is the purpose. As this new science progresses, every of us must determine how a lot we actually need to find out about ourselves.
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.![]()
Quotation:
The human physique has 37 trillion cells. If we are able to work out what all of them do, the outcomes might revolutionize well being care (2022, July 7)
retrieved 9 July 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-07-human-body-trillion-cells-results.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.









